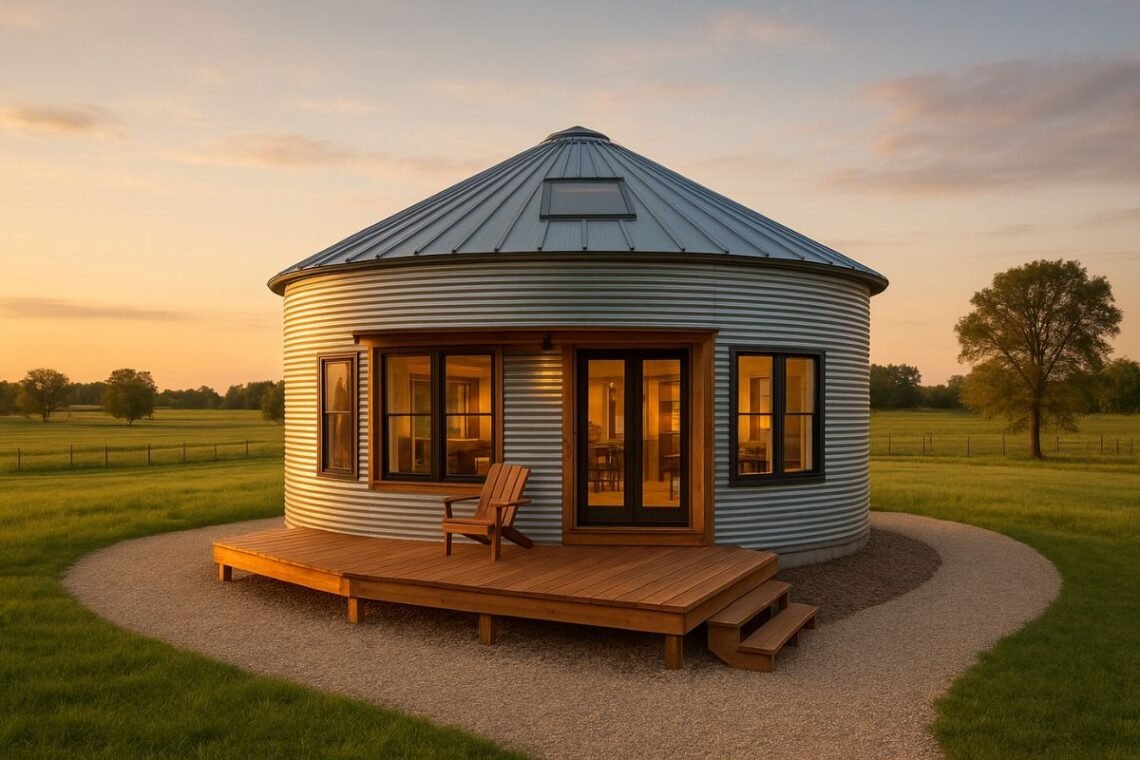
The grain bin house has quickly become one of the most popular budget-friendly housing solutions in 2025. With rising property prices and a shift toward sustainable, low-cost, and creative living, more people are transforming old farm grain bins into unique, modern, durable homes.
This guide is the most updated, beginner-friendly, and detailed resource available online. It covers every stage of the process:
- Choosing the right grain bin
- Regional cost considerations
- Step-by-step construction
- Safety and insulation
- Legal permits and lender challenges
- Floor plans
- Common mistakes
- Long-term maintenance
Plus, throughout the article, you’ll find visual references, beginner tips, and pro recommendations to make the process smoother.
1. What Is a Grain Bin House?
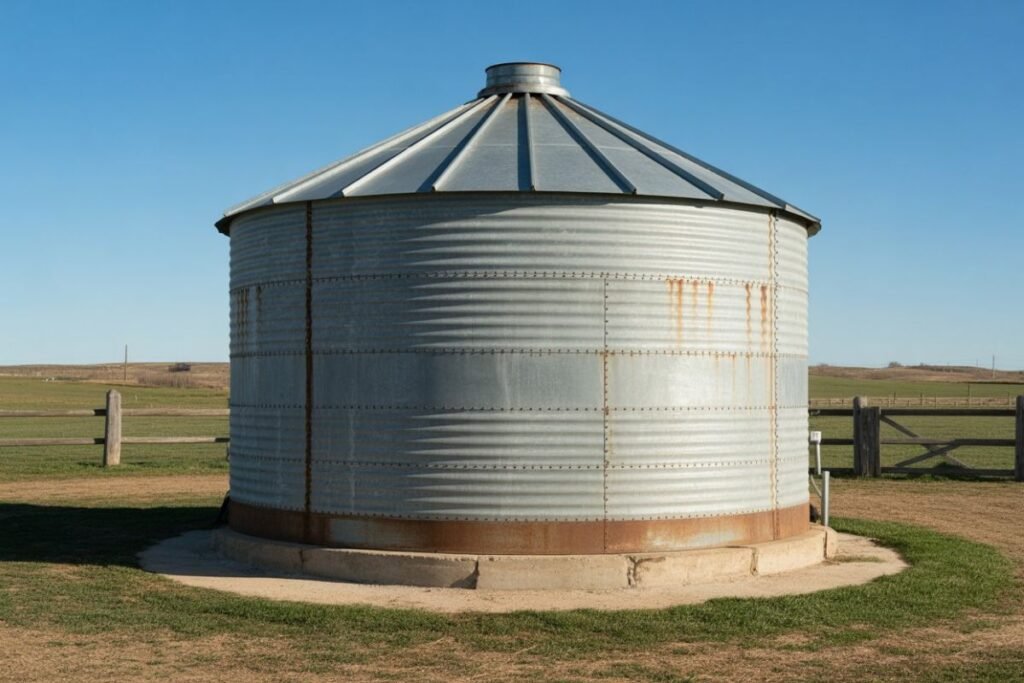

A grain bin house is a home built using a repurposed metal grain bin (or silo). These tall, round steel structures were originally made for storing grain, but their strength, durability, and affordability make them ideal building shells.
Why they are trending:
- Low cost of materials
- Eco-friendly reuse
- High wind resistance
- Minimal maintenance
- Unique round design
2. Benefits of Building a Grain Bin Home
- Budget-Friendly
Used bins may cost almost nothing. Even new bins cost less than conventional building materials.
- Extremely Durable
Steel withstands:
- strong winds
- moisture (with proper insulation)
- pests
- fire
- Fast Assembly
A used bin can be dismantled and reassembled in days.
- Sustainable
Reduces steel waste and construction footprint.
- Flexible Design
You can add:
- lofts
- skylights
- porches
- multi-bin homes
3. Important Things to Know Before You Start
Building Codes & Zoning (Varies by Region)
Before buying a bin or breaking ground:
- Check rural vs residential zoning
- Minimum dwelling size
- Insulation and fire code requirements
- Roof load capacity (especially in snowy regions)
Permits You May Need
- Foundation permit
- Electrical permit
- Plumbing permit
- Septic/water system approvals
- Occupancy certificate
Engineering Approval
Many areas require a structural engineer’s seal to approve:
- modified walls
- door/window cutouts
- multi-story designs
Lending Challenges (Important!)
Unconventional homes often face hurdles:
- Some banks avoid non-standard home builds
- Appraisals are difficult
- Mortgage options may be limited
Solution:
Look for lenders specializing in:
- barndominiums
- steel buildings
- agricultural conversions
- rural development loans
- or seller financing for land
4. Choosing the Right Grain Bin
New or Used?
Used Grain Bins
- Cost: free – $5,000
- Good for budget builders
- May require panel replacement
New Grain Bins
- Cost: $10,000 – $30,000
- No dents or rust
- Easier to modify
Regional Cost Variations
Material and contractor pricing varies significantly:
- Midwest USA: cheapest bins, lowest transport cost
- Southern USA: cheaper labor, higher humidity → better insulation needed
- Northern USA/Canada: pricier foundations because of frost lines
- Coastal areas: higher corrosion risk → additional coating needed
5. Step-by-Step Process: How to Build a Grain Bin House (Beginner + Expert Guide)
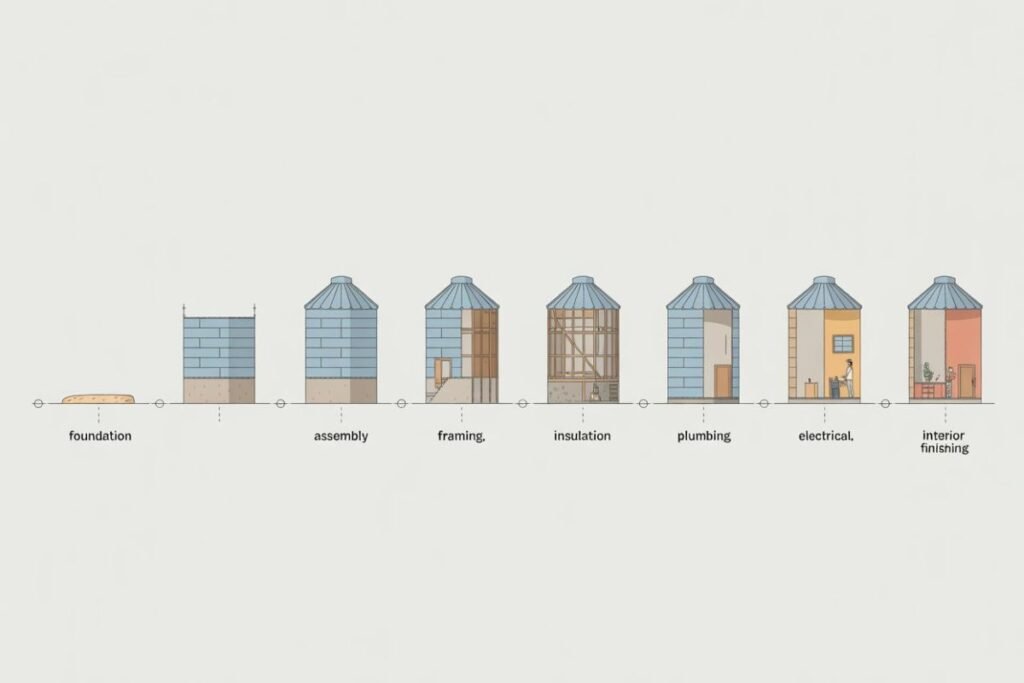
To make this easier to understand, each step includes:
- Beginner tip
- Pro builder tip
- Suggested visual
Step 1: Choosing Land
Pick land with:
- strong drainage
- sunlight exposure
- minimal wind funnel areas
- access to power/water
Beginner tip:
Avoid low-lying areas prone to flooding.
Step 2: Disassembling the Bin (If Used)
Tools:
- impact drills
- scaffolding
- safety harness
Beginner tip:
Label every panel and bolt during removal. This saves hours during reassembly.
Step 3: Laying the Foundation
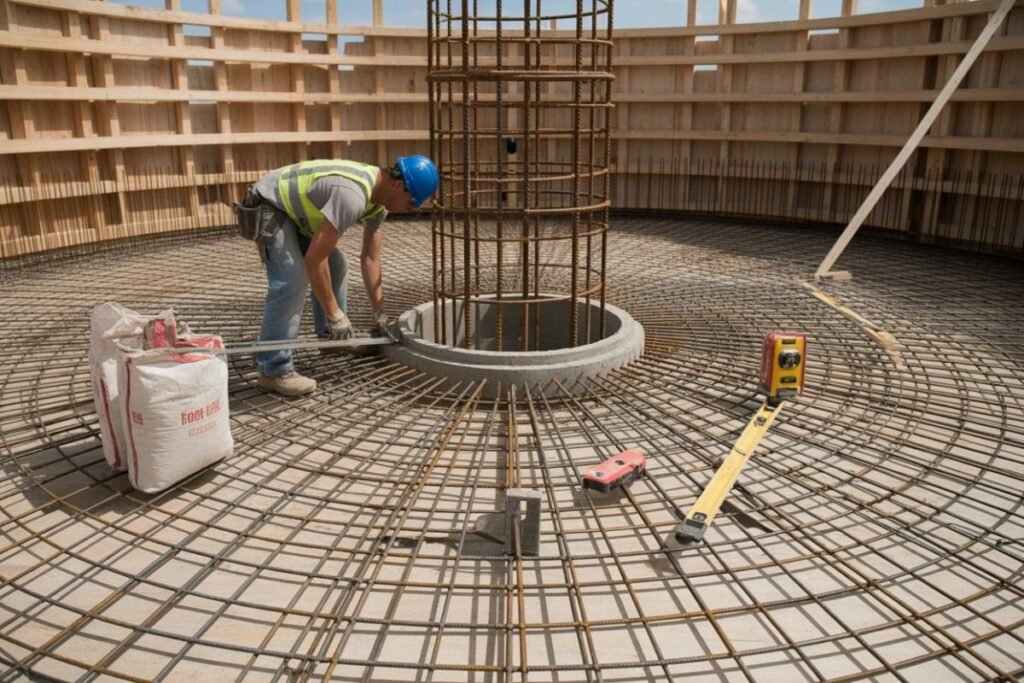

Grain bins require an extra-strong concrete slab.
Foundation Checklist:
- 6–12 inch slab
- rebar reinforcement
- perimeter anchor points
- moisture barrier
Regional note:
Cold climates require deeper footings because of frost heave.
Step 4: Reassembling the Bin
Rebuild from ground up using:
- bottom ring
- wall sheets
- roof panels
Pro tip:
Use new bolts even if old ones “look fine.”
Step 5: Cutting Doors & Windows
Cutting weakens structural integrity, so careful planning is essential.
Recommended placements:
- east for morning light
- south for winter heat
- avoid structural seams
Safety tip:
Support the wall with temporary framing before cutting.
Step 6: Framing the Interior
Round walls require special framing techniques.
Options:
- steel studs
- wood studs
- hybrid framing
Beginner tip:
Use flexible track framing for curved walls.
Step 7: Roof Upgrades
Options:
- skylight
- raised roof
- ventilation turbine
- full roof replacement
Skylights dramatically transform interior lighting.
Step 8: Insulation (Expanded & Improved Section)
Metal sweats. Insulation prevents condensation, heat buildup, and mold.
Here’s a detailed, improved comparison your competitor doesn’t have:
Best Insulation Options (2025 Comparison)
| Insulation Type | Pros | Cons | Best For |
| Closed-Cell Spray Foam | Highest R-value, waterproof, air-sealed | Most expensive | All climates, long-term homes |
| Rigid Foam Panels | Affordable, DIY-friendly | Gaps can form if not sealed well | Mild climates |
| Straw Bale | Eco-friendly, thick insulation | Requires thick interior framing | Off-grid builds |
| Denim Insulation | Eco-friendly, good soundproofing | Needs vapor barrier | Interior walls |
| Radiant Barrier + Foam (ZW Cable) | Reflects heat, ideal for hot climates | Not enough alone for cold areas | Southern USA |
Moisture & Condensation Prevention
Must include:
- vapor barrier
- vented roof
- foundation moisture barrier
- minimum insulation thickness
Step 9: Electrical Wiring
Use:
- conduit lines
- junction boxes
- LED fixtures
Round walls require curved routing plans.
Step 10: Plumbing Setup
Best layout strategy:
- keep kitchen, bathroom, laundry close together
- fewer wall penetrations = better structure and cost savings
Step 11: HVAC
Recommended:
- mini-split systems
- radiant floor heat
- heat pumps
Avoid oversized systems—steel heats quickly, so efficiency matters.
Step 12: Interior Finishing
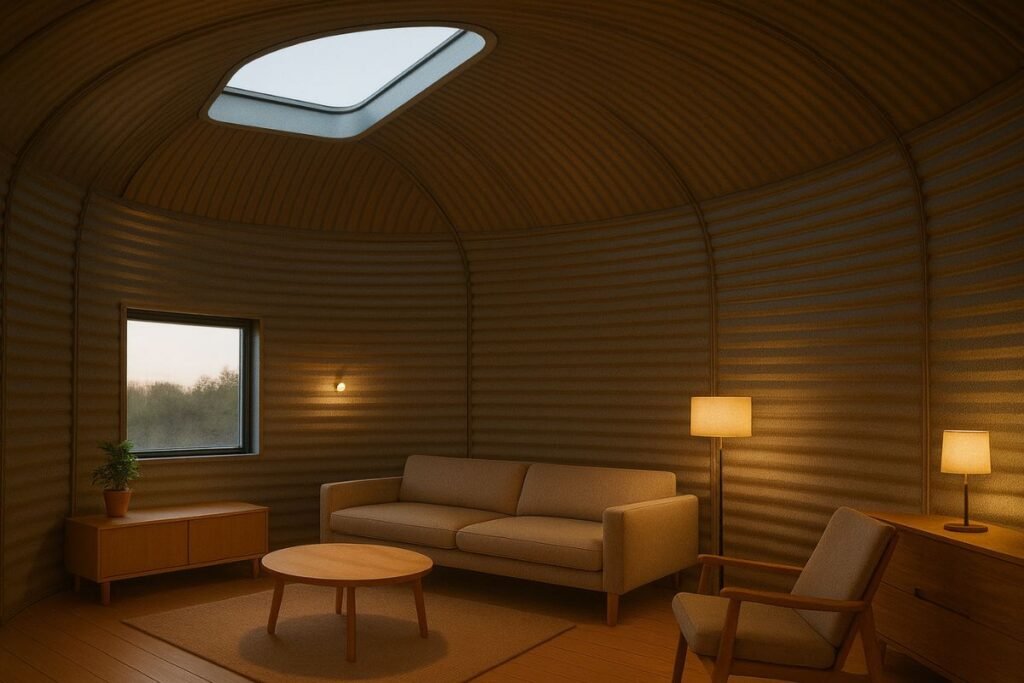

Popular choices:
- wood slat walls
- curved drywall
- plywood
- exposed steel + industrial lighting
Step 13: Exterior Enhancements
Ideas:
- circular deck
- pergola
- glass entryway
- multiple bins connected with breezeways
Step 14: Safety Features
Add:
- lightning grounding rod
- fireproof insulation
- emergency egress windows
6. Updated Cost Breakdown (With Regional Adjustments)
- DIY Build Cost:
$20,000 – $65,000
- Full Professional Build:
$90,000 – $250,000+
- Regional Price Factors:
- Midwest: cheapest materials
- West Coast: highest labor cost
- East Coast: highest permit fees
- Canada: higher insulation cost
- Southern USA: cheapest labor but requires humidity protection
7. Grain Bin House Floor Plans (With Visual Descriptions)
1-Bin Modern Studio
- open-plan living
- loft bedroom
- skylight center
2-Bin Connected Home
- one bin for living
- one for bedrooms
- glass hallway connector
3-Bin Large Family Layout
- central living bin
- bedroom wing
- utility/workshop wing
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Cutting too many openings
Weakens structure.
- Not using enough insulation
Leads to sweating, rust, mold.
- DIY electrical/plumbing without permits
Causes safety hazards + legal issues.
- Underestimating finishing costs
Interior finishing is the biggest expense.
9. Long-Term Maintenance (New Section)
Annual Tasks
- Inspect roof screws/bolts
- Check for rust spots (treat early)
- Test vapor barrier integrity
- Clean gutters/exterior vents
Every 5 Years
- Reseal foundation edge
- Repaint exterior steel to prevent corrosion
Pest Control
Steel walls protect against termites, but:
- seal all wall penetrations
- add screening to vents
10. FAQs
1. Are grain bin houses safe?
Yes. With proper foundation, insulation, and ventilation, they are very safe and sturdy.
2. How long do grain bin homes last?
Most last 50+ years with basic maintenance.
3. How much does it cost to build one?
Anywhere from $20,000 to $150,000+, depending on size and finish.
4. Can I build it myself?
Yes, if you have DIY skills. But you should hire pros for electrical, plumbing, and foundation work.
5. Do grain bin houses need special insulation?
Yes—closed-cell spray foam is the best option to prevent heat loss and condensation.
6. Can I get a loan for a grain bin house?
Financing is possible, but some banks require engineer-approved plans.
7. Are grain bin houses legal everywhere?
No. Check local building codes and zoning rules before starting.
8. What size bin is best for a home?
- 18–24 ft: tiny home
- 27–36 ft: 1–2 bedrooms
- 42–48 ft: large family home
9. What foundation do I need?
A circular reinforced concrete slab is the standard base.
10. Do they stay cool in summer?
Yes, with proper insulation and ventilation.
11. Can grain bin houses survive storms?
Yes. They are designed to withstand strong winds and heavy snow.
12. Are grain bin homes eco-friendly?
Yes. They reuse old metal bins and require fewer new materials.
13. Do they rust easily?
Not if you seal, inspect, and maintain them regularly.
Conclusion
A grain bin house is one of the most affordable, durable, and creative home-building options available in 2025. With proper planning, insulation, engineering safety, and maintenance, you can build a long-lasting home that costs far less than traditional construction.






